Electro-physiology and electro-therapeutics : showing the best methods for the medical uses of electricity / By Alfred C. Garratt.
482/740
- Publication/creation
- Boston : Ticknor and Fields, 1861.
- Physical description
- 3 unnumbered pages, 716 pages, 2 leaves of plates : illustrations ; 26 cm
- Contributors
-
Garratt, Alfred C. (Alfred Charles), 1813?-1891
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Notes
-
3d ed. has title: Medical electricity
Includes index and testimonials
- Type/technique
- Electronic books
- Subjects
-
Electrophysiology
Electrotherapeutics
- Attribution and usage
-
This material has been provided by the Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library at Yale University, through the Medical Heritage Library. The original may be consulted at the Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library at Yale University.
This work has been identified as being free of known restrictions under copyright law, including all related and neighbouring rights and is being made available under the Creative Commons, Public Domain Mark.
You can copy, modify, distribute and perform the work, even for commercial purposes, without asking permission.
The image contains the following text:
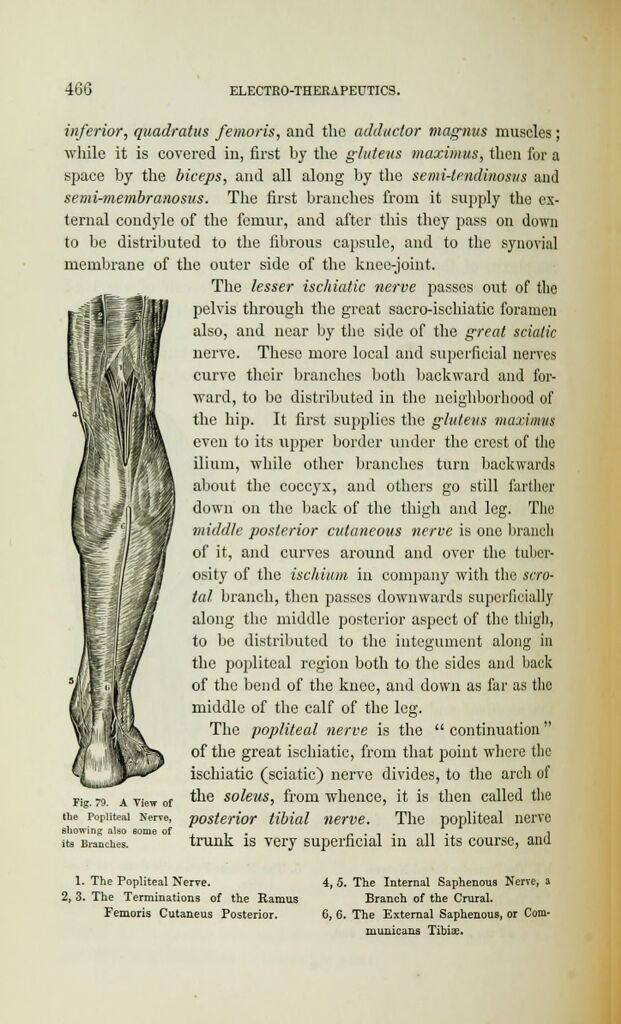
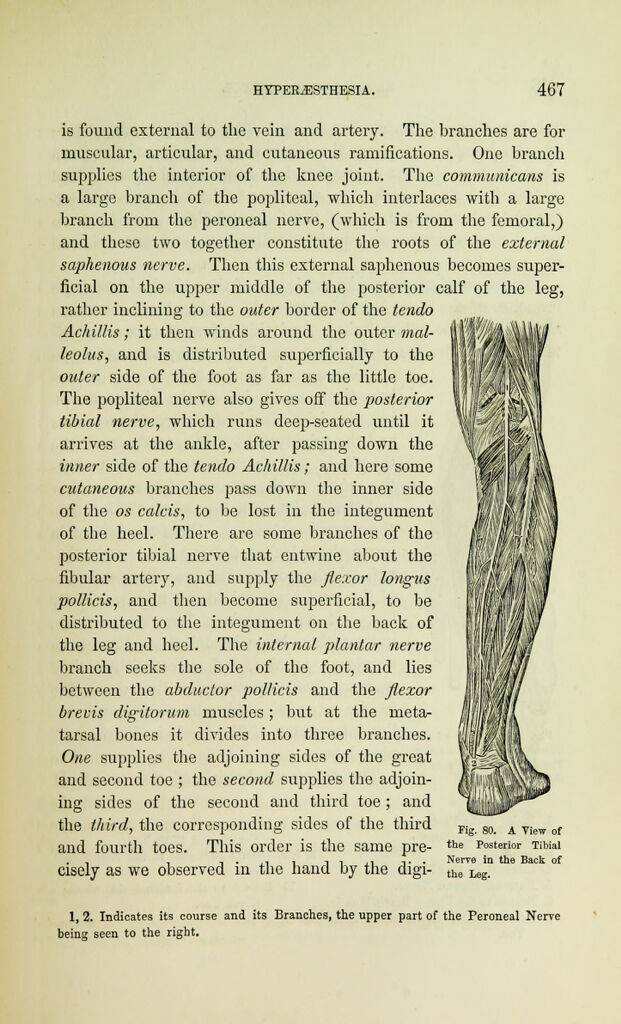
is found external to the vein and artery. The branches are for
muscular, articular, and cutaneous ramifications. One branch
supplies the interior of the knee joint. The communicans is
a large branch of the popliteal, which interlaces with a large
branch from the peroneal nerve, (which is from the femoral,)
and these two together constitute the roots of the external
saphenous nerve. Then this external saphenous becomes super-
ficial on the upper middle of the posterior calf of the leg,
rather inclining to the outer border of the tendo
Achillis; it then winds around the outer mal-
leolus, and is distributed superficially to the
outer side of the foot as far as the little toe.
The popliteal nerve also gives off the posterior
tibial nerve, which runs deep-seated until it
arrives at the ankle, after passing down the
inner side of the tendo Achillis; and here some
cutaneous branches pass down the inner side
of the os calcis, to be lost in the integument
of the heel. There are some branches of the
posterior tibial nerve that entwine about the
fibular artery, and supply the flexor longus
pollicis, and then become superficial, to be
distributed to the integument on the back of
the leg and heel. The internal plantar nerve
branch seeks the sole of the foot, and lies
between the abductor pollicis and the flexor
brevis digitorum muscles; but at the meta-
tarsal bones it divides into three branches.
One supplies the adjoining sides of the great
and second toe ; the second supplies the adjoin-
ing sides of the second and third toe; and
the third, the corresponding sides of the third Fig
and fourth toes. This order is the same pre- the Posterior Tibial
_ . , . ., . -, , ,. ,. . Nerve in the Back of
cisely as we observed in the hand by the digi- th6 Leg.
4IL
1, 2. Indicates its course and its Branches, the upper part of the Peroneal Nerve
being seen to the right.