Electro-physiology and electro-therapeutics : showing the best methods for the medical uses of electricity / By Alfred C. Garratt.
480/740
- Publication/creation
- Boston : Ticknor and Fields, 1861.
- Physical description
- 3 unnumbered pages, 716 pages, 2 leaves of plates : illustrations ; 26 cm
- Contributors
-
Garratt, Alfred C. (Alfred Charles), 1813?-1891
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Notes
-
3d ed. has title: Medical electricity
Includes index and testimonials
- Type/technique
- Electronic books
- Subjects
-
Electrophysiology
Electrotherapeutics
- Attribution and usage
-
This material has been provided by the Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library at Yale University, through the Medical Heritage Library. The original may be consulted at the Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library at Yale University.
This work has been identified as being free of known restrictions under copyright law, including all related and neighbouring rights and is being made available under the Creative Commons, Public Domain Mark.
You can copy, modify, distribute and perform the work, even for commercial purposes, without asking permission.
The image contains the following text:
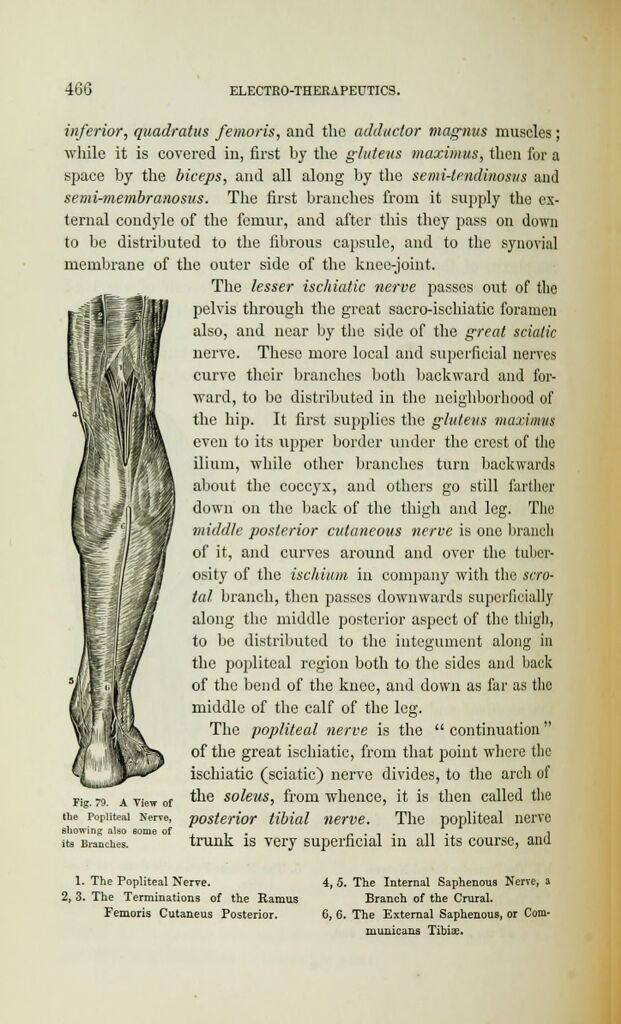
We must here notice again the obturator nerve, which arises
from the lumbar plexus, and with the obturator artery escapes
from the pelvis to supply first the obturator extermts, then pass-
ing in front of the adductor brevis muscle, supplying the adduc-
tor longus and the gracilis, and a branch ramifies the adductor
magnus; then, from this, a long cutaneous branch proceeds to
the plexus of the short saphenous nerve, and gives nervelets to
the integument all along the inner side of the calf of the leg;
but, before this, it gives some branches to the synovial mem-
brane on the posterior aspect of the knee joint.
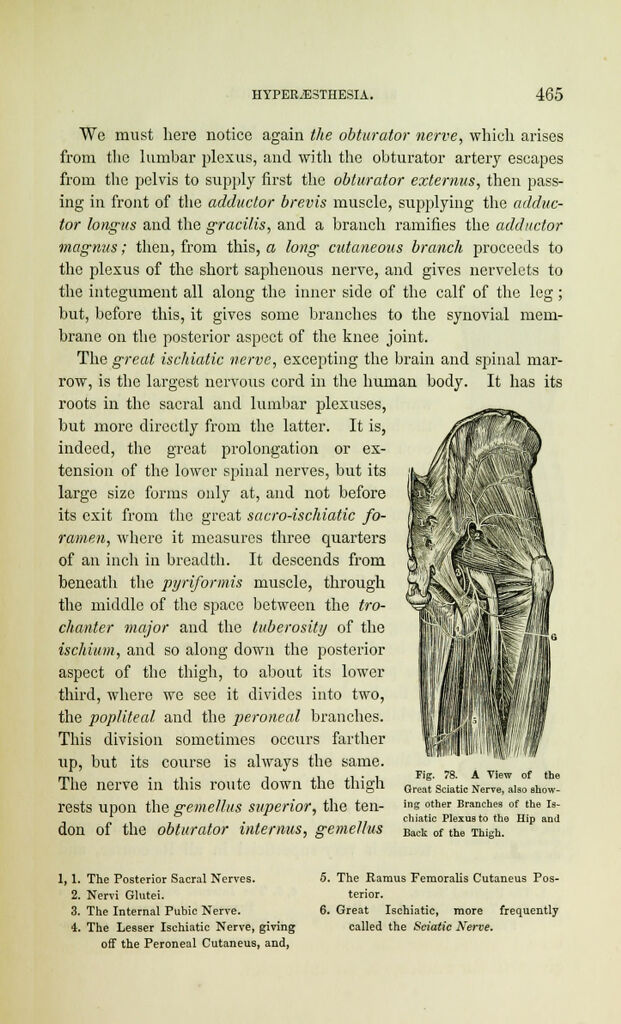
The great ischiatic nerve, excepting the brain and spinal mar-
row, is the largest nervous cord in the human body. It has its
roots in the sacral and lumbar plexuses,
hut more directly from the latter. It is,
indeed, the great prolongation or ex-
tension of the lower spinal nerves, but its
large size forms only at, and not before
its exit from the great sacro-ischiatic fo-
ramen, where it measures three quarters
of an inch in breadth. It descends from
beneath the pyriformis muscle, through
the middle of the space between the tro-
chanter major and the tuberosity of the
ischium, and so along down the posterior
aspect of the thigh, to about its lower
third, where we see it divides into two,
the popliteal and the peroneal branches.
This division sometimes occurs farther
up, but its course is always the same.
The nerve in this route down the thigh Grc£sciatic Nerves" show!
rests upon the gemellus superior, the ten- ins "then Branches of the u-
, chiatic Plexus to the Hip and
don of the obturator interims, gemellus BaCk of the Thigh.
1,1. The Posterior Sacral Nerves.
2. Nervi Glutei.
3. The Internal Pubic Nerve.
4. The Lesser Ischiatic Nerve, giving
off the Peroneal Cutaneus, and,
5. The Ramus Feraoralis Cutaneus Pos-
terior.
6. Great Ischiatic, more frequently
called the Sciatic Nerve.